This article is about one of the most hotly debated topics in the tech industry: the difference between cloud computing and on-premises computing. With the rapid adoption of AI and cloud technology, many people are wondering whether it’s time to ditch on-premises infrastructure altogether. In this blog post, we’ll shed light on the differences between these two approaches to computing and help you make an informed decision on which one to choose.
First, let’s define what cloud computing and on-premises computing are.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more, over the internet. In other words, instead of hosting all of these services on your own physical servers, you can access them through a third-party provider’s servers. This means you don’t need to invest in and maintain your own hardware, and you can easily scale up or down depending on your needs.
What is On-premises Computing?
On-premises computing, on the other hand, refers to the traditional approach of hosting your computing services on your own physical servers that are located on-site, typically in a data center. This means you have complete control over your infrastructure but also need to invest in and maintain your own hardware, software, and networking equipment.
What are the differences between cloud computing and on-premises computing?
Let’s take a closer look.
Let’s discuss more about the differences between cloud computing and on-premises computing with recent trends and stats.
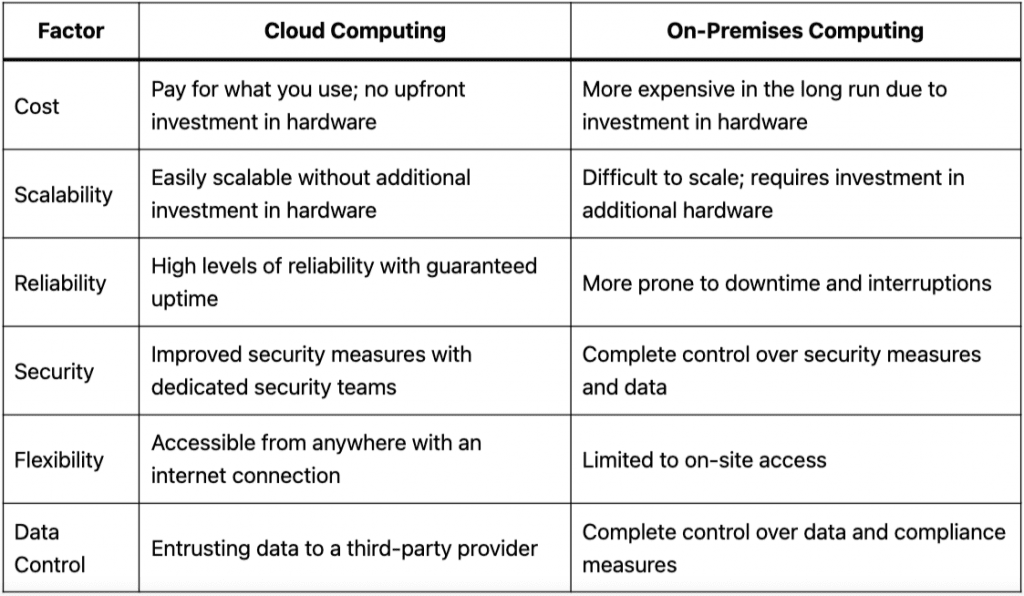
1. Cost
One of the primary benefits of cloud computing is that it can be more cost-effective than on-premises computing. With cloud computing, you only pay for what you use, and you don’t need to invest in expensive hardware and software upfront. This can be particularly beneficial for small and medium-sized businesses that don’t have the resources to build and maintain their own data centers.
According to a recent study by LogicMonitor, 87% of companies reported cost savings after moving to the cloud. On the other hand, on-premises computing can be more expensive in the long run, as you need to constantly invest in and maintain your own infrastructure.
2. Scalability
Scalability is another area where cloud computing has a significant advantage over on-premises computing. With cloud computing, you can easily scale up or down depending on your needs, without having to invest in additional hardware or software. This means you can quickly respond to changes in demand, whether that’s scaling up to handle a surge in traffic or scaling down during slower periods.
On-premises computing, on the other hand, can be more difficult to scale. You need to invest in additional hardware and software to support increased demand, and it can take time to set up and configure new servers.
3. Reliability
Reliability is another factor to consider when choosing between cloud computing and on-premises computing. Cloud providers typically offer high levels of reliability, with many guaranteeing 99.99% uptime. This means your applications and data are always available when you need them, without any downtime or interruptions.
On-premises computing, on the other hand, can be more prone to downtime and interruptions. If your hardware fails or there’s a power outage, you could experience significant downtime that can impact your business operations.
4. Security
Security is a concern for any organization, and it’s an area where on-premises computing has traditionally had an advantage over cloud computing. With on-premises computing, you have complete control over your infrastructure and can implement your own security measures to protect your data.
However, cloud providers have made significant strides in recent years to improve their security measures. Many offer advanced security features, such as multi-factor authentication, encryption, and network segmentation.
According to a study by Cloud Security Alliance, 64% of IT professionals believe the cloud is as secure or more secure than on-premises computing. Additionally, cloud providers have dedicated security teams that can focus solely on identifying and mitigating potential security threats.
5. Flexibility
Flexibility is another factor to consider when choosing between cloud computing and on-premises computing. Cloud computing allows you to access your applications and data from anywhere with an internet connection, making it ideal for remote work or for businesses with multiple locations.
On-premises computing, on the other hand, requires you to be on-site to access your applications and data. This can limit your flexibility and make it more difficult to work remotely or collaborate with colleagues in other locations.
6. Data Control
Another factor to consider when choosing between cloud computing and on-premises computing is data control. With on-premises computing, you have complete control over your data and can ensure that it’s stored and handled in compliance with your organization’s policies and regulations.
With cloud computing, however, you’re entrusting your data to a third-party provider. This means you need to carefully evaluate their security and compliance measures to ensure they meet your organization’s needs.
Recent Trends in Computing
Cloud computing has seen tremendous growth in recent years, with more and more businesses moving their operations to the cloud. According to a report by Gartner, global spending on cloud services is expected to reach $591.8 billion in 2023, up from $490.3 billion in 2022.
One reason for this growth is the increased adoption of hybrid cloud solutions, which allow businesses to leverage both cloud and on-premises infrastructure. This allows businesses to take advantage of the benefits of both approaches while minimizing their drawbacks.
Another trend is the adoption of multi-cloud solutions, where businesses use multiple cloud providers for different applications and services. This helps to mitigate the risk of downtime and ensures that businesses have access to the best features and services from each provider.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the choice between cloud computing and on-premises computing depends on a variety of factors, including cost, scalability, reliability, security, flexibility, and data control. Cloud computing can be more cost-effective, scalable, and reliable, while on-premises computing can offer greater control and security.
However, recent trends in the industry suggest that businesses are increasingly adopting hybrid and multi-cloud solutions to take advantage of the benefits of both approaches. Ultimately, the choice between cloud computing and on-premises computing should be based on the specific needs and goals of your organization.


