As consumers, we often find ourselves taking out loans to finance various purchases, whether it’s a car, a home, or a personal loan for a large expense. When we take out these loans, we’re faced with the task of understanding the terms and conditions of the loan, including the repayment schedule. Two common repayment methods that are often used are installment payments and amortization payments. In this article, we’ll explore the differences between these two repayment methods and how they can affect the total cost of the loan.
Understanding Installment Payments
Installment payments are a form of loan repayment where the borrower pays a fixed amount of money over a set period. The borrower and the lender agree on a repayment schedule, which includes the loan amount, the interest rate, and the duration of the loan. The borrower makes a fixed payment each month until the loan is paid off in full.
One common example of an installment loan is an auto loan. Let’s say you take out a $25,000 auto loan with a 5-year repayment term and an interest rate of 3.5%. The loan will be divided into 60 equal payments of $450.65. Each payment will consist of a portion of the principal loan amount and the interest accrued on that loan amount.
Understanding Amortization Payments
Amortization payments are also a form of loan repayment, but they work a bit differently than installment payments. With an amortization loan, the borrower makes payments that include both the principal and the interest. Unlike installment loans, the amount of the payment will change over time.
One common example of an amortization loan is a home mortgage. Let’s say you take out a $200,000 mortgage with a 30-year repayment term and an interest rate of 4.0%. The loan will be divided into 360 monthly payments of $955. The first payment will consist of mostly interest, but as you continue to make payments, more of the payment will go toward the principal loan amount.
Differences between Installment and Amortization Payments
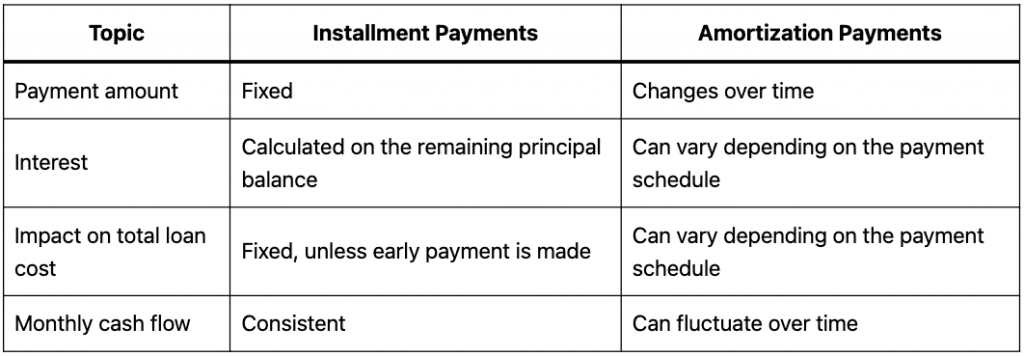
Here’s a table summarizing the key differences between installment and amortization payments:
Payment Amount
The primary difference between installment and amortization payments is how the payments are calculated. With installment payments, the payment amount is fixed, whereas with amortization payments, the payment amount changes over time. This means that with an amortization loan, you’ll pay more interest at the beginning of the loan term and more principal toward the end of the term.
Interest
Another key difference is how the interest is calculated. With installment loans, the interest is typically calculated based on the outstanding balance of the loan. With amortization loans, the interest is calculated based on the remaining principal balance of the loan. This means that as you make payments on an amortization loan, the interest portion of the payment will decrease as the principal balance decreases.
Impact on Total Loan Cost
The repayment method you choose can have a significant impact on the total cost of the loan. With an installment loan, the total cost of the loan is typically fixed from the beginning. With an amortization loan, the total cost of the loan can vary depending on how quickly you pay off the loan.
For example, let’s say you take out a $50,000 personal loan with a 5-year repayment term and an interest rate of 10%. If you make installment payments of $1,050 per month, the total cost of the loan will be $63,000. However, if you make amortization payments of $1,110 per month, the total cost of the loan will be $66,600. This is because you’re paying more in interest with the amortization loan.
Monthly cash flow
In addition to the impact on total loan cost, the repayment method can also affect your monthly cash flow. With an installment loan, the payment amount is fixed, which can make budgeting easier. With an amortization loan, the payment amount can change over time, which can make budgeting more challenging.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the differences between installment and amortization payments is important for anyone considering taking out a loan. The repayment method you choose can have a significant impact on the total cost of the loan and your monthly cash flow. Installment payments are a form of loan repayment where the borrower pays a fixed amount of money over a set period, while amortization payments are a form of loan repayment where the borrower makes payments that include both the principal and the interest, and the payment amount changes over time. By understanding the differences between these two repayment methods, you can make a more informed decision when it comes to taking out a loan.


