In today’s crowded marketplace, brands must coordinate touchpoints to effectively engage consumers. Integrated marketing communications (IMC) brings synergy to promotional efforts for unified messaging and greater impact. By skillfully combining various tactics, marketers can amplify awareness, shape perceptions, and drive loyalty. This article explores core IMC tools that can be strategically orchestrated to attract and convert customers.
What are Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) Tools?
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC) tools refer to the promotional mix elements used to drive integrated campaigns. Core IMC tools include advertising, public relations, direct marketing, sales promotions, personal selling, and sponsorships. Additional emerging tactics like social media marketing, mobile marketing, and online content also play a key role.
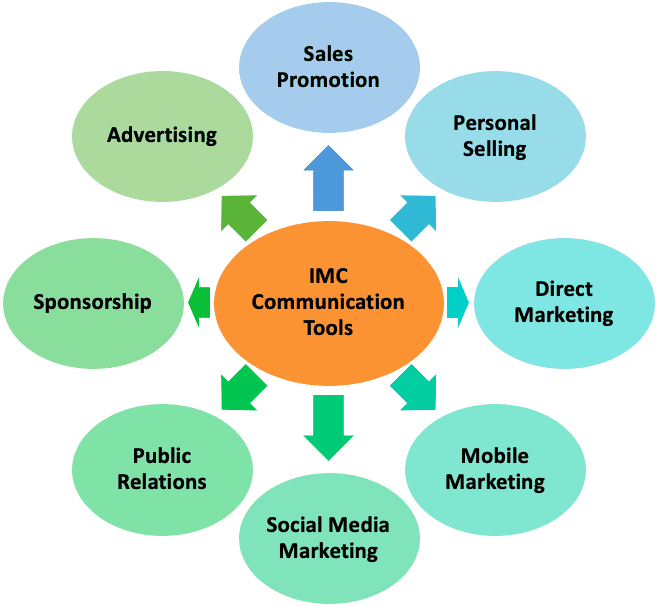
The idea behind IMC is to coordinate these tools to create unified and seamless messaging. This amplifies reach and impact across channels, as audiences receive reinforced touchpoints for a consistent brand experience. IMC requires marketers to strategically orchestrate traditional and digital tactics to convey value, increase visibility, and ultimately drive engagement and sales.
8 Integrated Marketing Communications Tools for Driving Growth
Integrated marketing communications (IMC) synchronizes messaging across multiple promotional channels to create a seamless brand experience. By combining various tactics, marketers can effectively communicate their value proposition, boost brand awareness, and increase sales. Let’s examine some key IMC tools:
1. Advertising
Advertising broadcasts messages to a broad audience through media like print, radio, television, and digital platforms. Ads can rapidly increase brand visibility and associate brands with desired impressions. Creative advertising also engages audiences emotionally to build brand loyalty.
2. Personal Selling
Through person-to-person outreach, sales teams can directly address prospect needs and nurture relationships. Personal selling allows for customized conversations to overcome objections and convey value.
3. Direct Marketing
Direct mail, email, SMS, and other direct channels enable targeted, measurable communication. Marketers can track responses to optimize and expand direct marketing programs.
4. Mobile Marketing
With widespread mobile device usage, brands can reach customers on the go through SMS, mobile apps, and other portable touchpoints. Mobile’s always-on nature makes it ideal for time-sensitive promotions.
5. Social Media
Social platforms like Facebook and Twitter facilitate meaningful conversations with current and potential customers at scale. Brands can boost engagement through social listening, content creation, and community management.
6. Public Relations
PR activities like press releases, events, and spokesperson partnerships shape positive brand narratives through third-party validation. This earned media provides high-credibility endorsements.
7. Sales Promotions
Tactics like coupons, contests, and loyalty programs incentivize purchases. Sales promotions encourage trial use and repeat business.
8. Sponsorships
Sponsoring events, causes, and influencers taps into associated passions. Sponsorships boost brand exposure while also demonstrating social responsibility.
What is the purpose of IMC tools?
The purpose of IMC tools is to coordinate messaging across marketing channels to create consistent and impactful brand experiences. IMC provides an orchestrated approach to engage customers and drive business results.
What are IMC examples?
Integrated marketing communications (IMC) synchronizes promotional efforts like advertising, direct marketing, social media, PR, sales promotions, and more. Some examples include:
- Running a coordinated ad campaign with corresponding social media content and email nurturing
- Aligning in-store promotions with external advertising and direct mail offers
- Sponsoring an event to generate buzz and media impressions
Some key benefits of IMC
- Strengthened brand identity and positioning – IMC creates consistent messaging that clearly conveys what a brand stands for. It aligns visual identity, tone, and values across channels to build a recognizable and unique brand image.
- Improved efficiency and return on marketing investment – By linking campaigns across channels, marketers can maximize results from budgets. IMC eliminates redundant efforts and focuses spend on tactics that best reach and resonate with audiences.
- Enhanced customer experiences across touchpoints – Customers engage with brands across many access points. IMC connects these interactions to create a seamless, cohesive journey.
- Greater reach and impact across audiences – Coordinated IMC expands a brand’s reach by promoting across multiple platforms. It also creates repetition to increase message absorption and conversion.
Steps involved in implementing an IMC strategy
- Identify target audiences – Define key customer segments and buyer personas you aim to reach. Understand their demographics, psychographics, needs, media habits, etc.
- Determine marketing objectives – Set specific goals like increasing brand awareness by X% or boosting sales by Y%. Objectives should link to larger business goals.
- Map out customer journeys – Chart how audiences interact with the brand across channels as they move through awareness, consideration, and conversion.
- Audit existing assets/channels – Take stock of current marketing initiatives and assets usable for IMC. Assess reach and performance.
- Develop synchronized messaging – Create consistent positioning and messaging that resonates across channels.
- Execute coordinated campaigns – Develop synchronized campaigns with aligned timing, offers, visuals, and captions.
- Analyze results and optimize – Evaluate campaign KPIs to identify high-performing platforms and creative. Refine strategy.
Challenges or disadvantages of IMC
- Integration complexity – Sophisticated coordination across many moving parts can be difficult.
- Resource requirements – IMC needs staff, tools, and budgets to collaborate across departments.
- Difficulty measuring synergistic effects – Isolating the impact of integrated efforts from other factors can be tough.
- Need for organizational alignment – IMC requires company-wide vision and cooperation between teams. Silos can hamper efforts.
Measuring the effectiveness of an IMC program
- Brand awareness and perception studies – Measure how IMC affects brand sentiment and attributes.
- Lead generation and sales lift analyses – Quantify sales and pipeline impact of IMC efforts.
- Traffic and engagement metrics – Track website visits, social shares, contest entries, etc.
- Win/loss and customer satisfaction research – Survey customers on marketing influence in purchase decisions.
- Message consistency surveys – Gauge if audiences perceive consistent branding across channels.
An integrated approach combining these tactics amplifies impact across channels. Streamlined IMC aligns touchpoints to effectively attract, engage, and nurture customers.